Healthy Diet For Heart

Healthy Diet For Heart
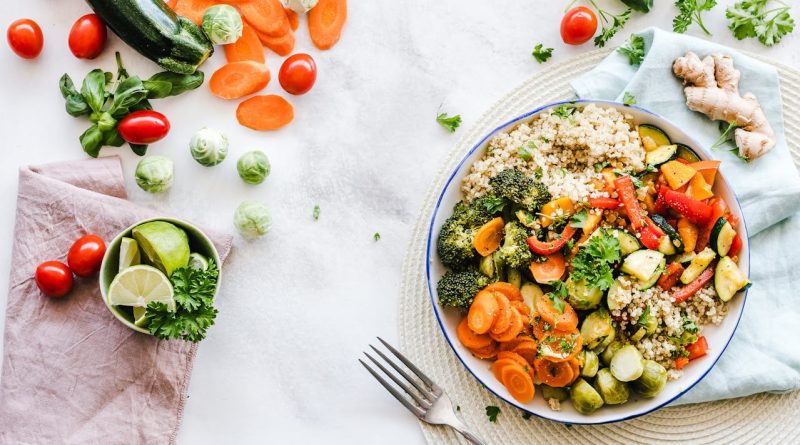
A healthy diet is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death globally, but with mindful eating, you can significantly reduce your risk. The right diet can help control blood pressure, reduce inflammation, manage weight, and improve overall cardiovascular health. This guide will walk you through the key components of a heart-healthy diet, offering practical tips and easy-to-follow advice.
Understanding Heart-Healthy Nutrients
Fiber
Fiber is essential for heart health. It helps lower cholesterol levels and maintain healthy blood pressure. Soluble fiber, found in oats, beans, lentils, fruits, and vegetables, is particularly effective at reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol. Aim to include at least 25-30 grams of fiber in your daily diet.
Healthy Fats
Not all fats are bad. Unsaturated fats, found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish, can actually benefit your heart. These fats help reduce bad cholesterol levels and increase good cholesterol. Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats, which are found in red meat and full-fat dairy products.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, have been shown to reduce inflammation and lower the risk of heart disease. Plant sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts also provide omega-3s.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, play a role in protecting your heart. They combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation. Fruits and vegetables, especially berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens, are rich in antioxidants.
Key Dietary Components
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables should form the cornerstone of your diet. They are low in calories and high in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Aim to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables at each meal. Choose a variety of colors to ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients.
Whole Grains
Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, barley, and whole-wheat products, are excellent sources of fiber and other nutrients that play a role in regulating blood pressure and heart health. Replace refined grains with whole grains to improve your diet.
Lean Proteins
Choose lean protein sources to support heart health. Fish, poultry, beans, legumes, and tofu are excellent options. Limit red meat and processed meats, which are high in saturated fats and sodium.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are packed with healthy fats, protein, and fiber. Eating a handful of unsalted nuts daily can improve heart health. Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are particularly beneficial.
Dairy
Opt for low-fat or fat-free dairy products to reduce your intake of saturated fats. Yogurt, milk, and cheese can be part of a heart-healthy diet if chosen wisely.
Healthy Eating Patterns
The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is renowned for its heart-health benefits. It emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and olive oil. It also includes moderate consumption of fish and poultry. This diet is rich in healthy fats and antioxidants, promoting cardiovascular health.
The DASH Diet
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet focuses on reducing sodium intake and increasing the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy. It is particularly effective for lowering blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease.
Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets, including vegetarian and vegan diets, eliminate or reduce animal products. They are typically high in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats while being low in saturated fats and cholesterol. A well-planned plant-based diet can offer significant heart-health benefits.
Practical Tips for Heart-Healthy Eating
Plan Your Meals
Meal planning can help you make healthier choices. Plan your meals around fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. This approach ensures you have heart-healthy ingredients on hand and reduces the temptation to eat unhealthy foods.
Read Food Labels
Reading food labels helps you make informed choices. Look for products low in saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium. Check the fiber content and choose options that are higher in fiber.
Control Portion Sizes
Portion control is key to maintaining a healthy weight and heart. Use smaller plates, and be mindful of serving sizes, especially for high-calorie foods.
Cook at Home
Cooking at home allows you to control the ingredients in your meals. Use heart-healthy cooking methods such as grilling, steaming, baking, and sautéing with minimal oil. Avoid frying and heavy use of butter or cream.
Limit Sugar Intake
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to heart disease. Limit sugary drinks, sweets, and processed foods high in added sugars. Opt for natural sweeteners like fruits when you need a sweet fix.
Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for overall health, including heart health. Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Limit caffeinated and sugary beverages.
Foods to Avoid
Trans Fats
Trans fats increase bad cholesterol and lower good cholesterol. They are found in many fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks. Avoid products with “partially hydrogenated oils” on the ingredient list.
High-Sodium Foods
High sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease. Limit processed foods, canned soups, deli meats, and salty snacks. Cook with herbs and spices instead of salt.
Red and Processed Meats
Red meat and processed meats are high in saturated fats and sodium. Limit consumption of beef, pork, lamb, sausages, and hot dogs. Opt for leaner meats like chicken or fish.
Sugary Beverages
Sugary beverages like soda and fruit juices contribute to weight gain and diabetes, both of which are risk factors for heart disease. Choose water, herbal tea, or unsweetened drinks instead.
Incorporating Exercise
A heart-healthy diet works best when paired with regular exercise. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Activities like walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging can improve cardiovascular health.
Managing Stress
Stress management is also vital for heart health. Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy eating habits and increase the risk of heart disease. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies that you enjoy.
Monitor Your Health
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help you keep track of your heart health. Monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and weight. Make necessary adjustments to your diet and lifestyle based on your health metrics.
A heart-healthy diet is achievable with mindful choices and a balanced approach to eating. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, controlling portions, and avoiding harmful ingredients, you can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease. Combine your diet with regular exercise and stress management for optimal heart health. Remember, small changes can make a big difference. Start today for a healthier heart tomorrow.